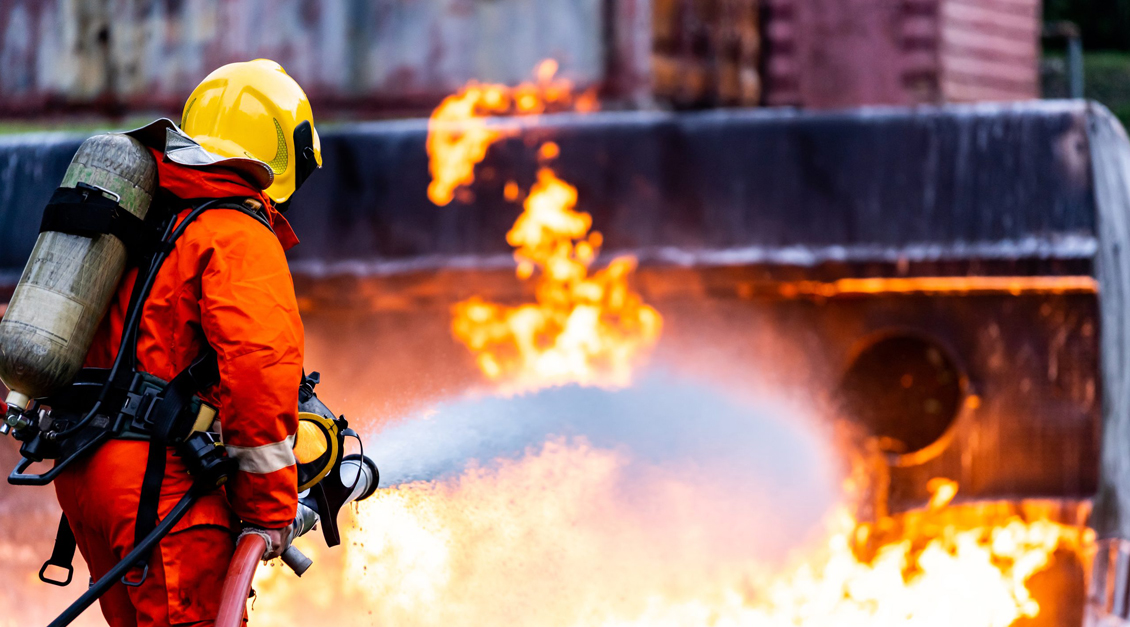
Enhancing Systems for a Safer Future
Process safety and safety engineering are vital disciplines in designing and managing systems to ensure safety, prevent accidents, and mitigate risks across industries like nuclear power, aviation, and manufacturing. These fields focus on protecting workers, the public, and the environment while maintaining efficient operations. By integrating process safety and safety engineering, industries can achieve reliable performance, reduced risks, and optimized costs.
What is process Safety Engineering?
Safety engineering is an essential practice that designs systems to operate safely, minimizing the chances of accidents and their consequences. It’s especially critical in high-risk sectors where failures could be catastrophic.
Process safety, a key component of safety engineering, emphasizes preventing incidents like leaks, explosions, or equipment failures by analyzing and controlling hazards. Together, process safety and safety engineering use tools like qualitative and quantitative analysis to identify risks and ensure systems remain safe even during component failures.

- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly inspecting and maintaining systems to uphold safety engineering standards and ensure ongoing process safety.
Core Components of Safety Engineering
Safety engineering relies on several foundational elements to enhance process safety:
- Hazard Identification: Spotting potential dangers using techniques like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) to bolster process safety.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating hazard likelihood and impact through probabilistic methods to prioritize safety engineering measures.
- Design for Safety: Embedding features like redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms into systems to strengthen process safety.
How Safety Engineering Boosts Performance
Safety engineering enhances system performance by reducing downtime and increasing reliability. In manufacturing, for instance, process safety measures prevent accidents that could halt production, ensuring consistent output. By identifying hazards early, safety engineering eliminates the need for emergency repairs, while efficient designs—like passive safety systems in nuclear plants—improve operational reliability. This synergy between process safety and safety engineering delivers steady performance, proving that safety can drive efficiency, not just add costs.
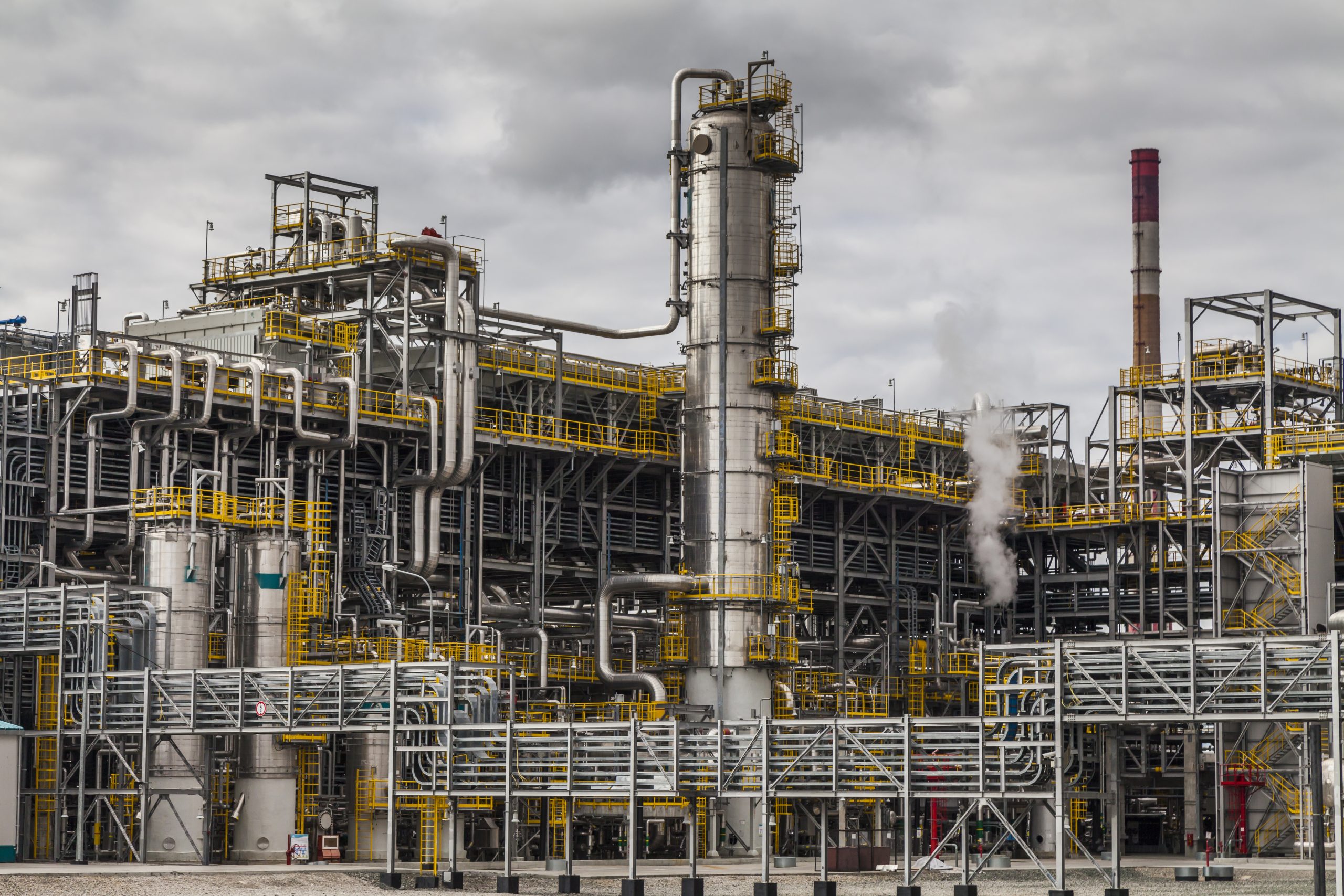

Reducing Risks with Process Safety Engineering
Risk reduction is a cornerstone of process safety and safety engineering. Through systematic hazard analysis and risk assessments, these disciplines identify vulnerabilities and implement preventive measures. Safety engineering introduces design enhancements like redundancy and fail-safe systems, while process safety ensures proper training and controls to manage risks. In nuclear power plants, containment structures and emergency core cooling systems exemplify how safety engineering and process safety work together to minimize risks, such as radioactive releases, safeguarding both people and the environment.
Optimizing Costs Through Safety Engineering
Safety engineering optimizes costs by preventing accidents that lead to expensive repairs, legal penalties, and downtime. Process safety contributes by designing efficient systems that lower long-term maintenance expenses. Risk assessments in safety engineering prioritize cost-effective solutions, ensuring resources are used wisely. For example, in nuclear facilities, advanced safety engineering features like accident-tolerant fuels reduce maintenance needs and incident-related costs, demonstrating that investing in process safety and safety engineering yields significant savings over time.
Real-World Application: Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants showcase the impact of process safety and safety engineering. Advanced reactors incorporate passive cooling systems and accident-tolerant fuels, reflecting cutting-edge safety engineering principles. These features improve performance by ensuring reliable power generation, reduce risks with multiple safety barriers, and optimize costs by minimizing maintenance and accident expenses. Process safety ensures these systems are monitored and controlled, preventing incidents that could disrupt operations or harm the environment.
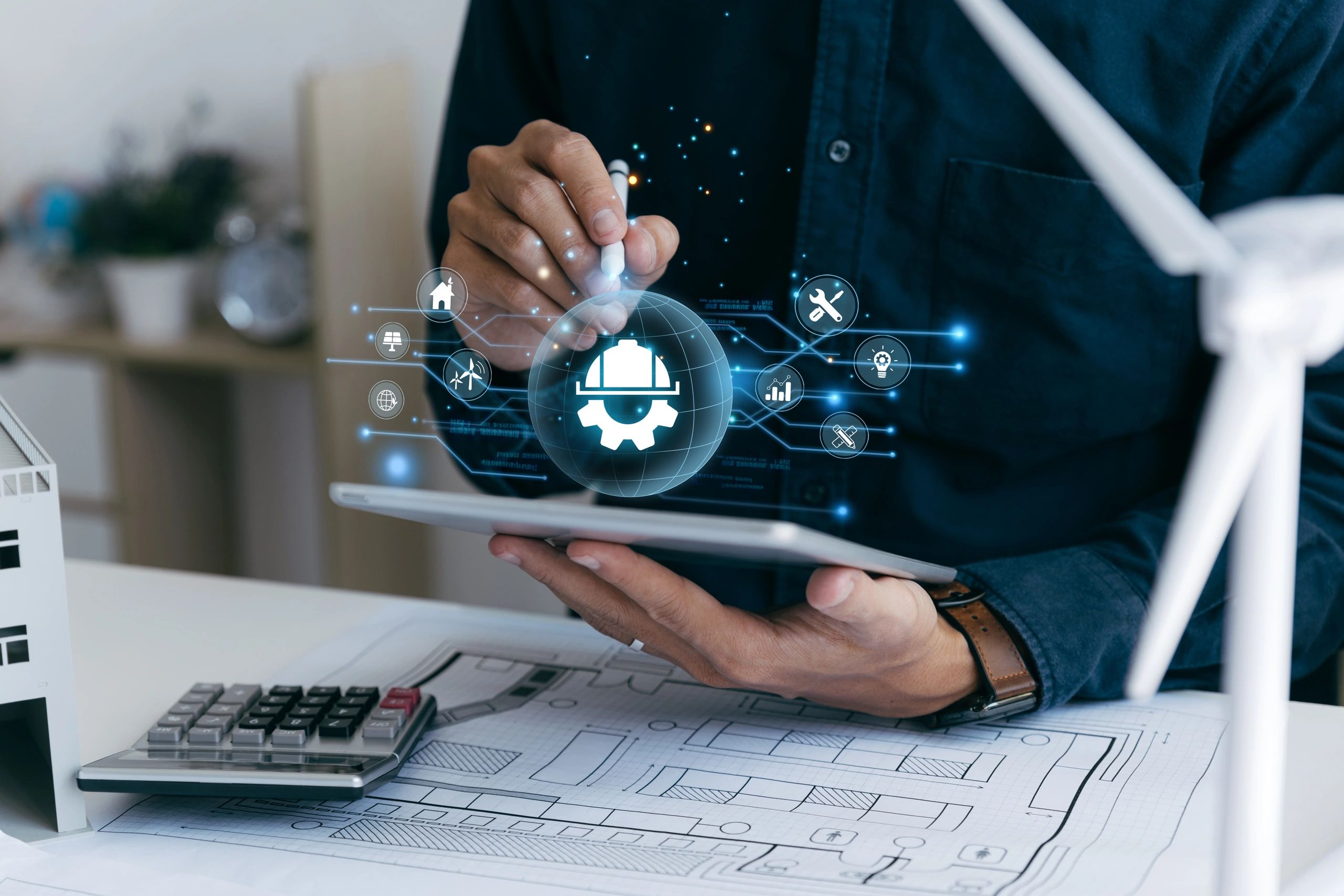

The Strategic Value of Process Safety Engineering
Process safety and safety engineering are evolving with innovations like artificial intelligence, IoT, and digital twins, enabling real-time risk monitoring and predictive maintenance. These advancements enhance process safety by anticipating issues before they arise, while safety engineering integrates them into system designs. For businesses, prioritizing process safety and safety engineering ensures compliance with regulations, boosts competitiveness, and supports sustainable operations in high-stakes industries.
The Power of Process Safety Engineering
Process safety and safety engineering deliver measurable benefits—improved performance, reduced risks, and optimized costs. From nuclear reactors to manufacturing floors, these disciplines create systems that are safe, efficient, and cost-effective. By embracing process safety and safety engineering, industries pave the way for a safer, more reliable future, proving their indispensable role in modern operations.